Heavy Railways
| Accra-Tema Railway Line | ||

Oil-burning locomotive train stationed at Accra in 1974. |

Engine No. 1670 of Ghana Railways. |

Railway station of Kumasi, Ghana. |
| Airdrie-Bathgate Railway Link | ||

The original Airdrie-Bathgate rail line was closed in 1956, but the Scottish Government has now decided to reopen and upgrade the line. |

The line will connect Edinburgh and Glasgow, also passing through Drumgelloch on the way. |

Trains on the Airdrie-Bathgate line will run at speeds of up to 80mph. |
| Alameda Corridor Freight Line, | ||
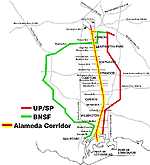
The Alameda Corridor Route Map. |

The aggressive-looking BNSF Dash-9 locomotive design has been adopted as standard for the heaviest freight trains which will use the Alameda Corridor. |

A panoramic view of the nerve centre of BNSF operations, its network operations centre at Fort Worth, Texas. |

A Union Pacific Freight Train hauls its cargo over one of the many bridges along the Alameda Corridor route. |

A hybrid diesel/battery locomotive – the ‘Green Goat’ - has been trialed by ACTA in order to determine how much air pollutants from the ports rail activity can be reduced. |

The centerpiece of the Alameda Corridor is this 33m deep cutting, which takes the line straight into the ports without causing congestion on the surface. |

Container trains form the bulk of freight services. Here a long rake of double-stack container snakes through the suburbs. |

A container train takes the new alignment through the 16km trench that has saved trains crossing 200 level crossings on the short 32km route to the ports. |
|
| Alice Springs-Darwin Rail Line | ||

Trains began running on the new line in January 2004. |

Tracklaying on the bridge over Fergusson River. |

The heaviest locomotives can be used on the Alice Springs line. |

Thousands of tonnes of track ballast have had to be brought to the railway site. |

Bridge beams cast at Palmerston. |

Buchanan Camp workers celebrate after completion of the final Thermit track weld. |

Freightlink Class GT46C for Darwin-Alice Springs completion. |
||
| Antwerpen Centraal and North South Junction | ||
The project added new levels and a through route. |

The station had to be heavily reworked to meet modern passenger expectations. |

The station remained open whilst the works progressed. |

The new atrium provides natural ventilation and light to all levels. |

Level -2 handles local and international trains like Thalys and Amsterdam-Brussels Benelux services. |

The original level, now '+1', has six lengthened platforms. The brick-faced Level -1 beneath has four new terminus platforms. |

As viewed, the left tracks are for Centraal lower levels; an Intercity service leaves the viaduct for the original platforms; avoiding lines to the right. |

Antwerp's extensive freight traffic uses the avoiding line around the east of the city centre. |

Beyond the north tunnel portal, the new line rises to pass over the Albert Canal and rejoin the alignment of the avoiding line. |

Beyond Antwerpen-Luchtbal the new line connects with the high-speed route and the original line to the Netherlands. |
||
| Bahn 2000 | ||

Swiss Federal Railway's 15-year Bahn 2000 investment project has invested heavily in new infrastructure and new trains. |

A Lok 2000 locomotive. |

The Lok 2000 locomotives carry distinctive branding associating them with the Bahn 2000 project. |

The Base tunnel at St. Gotthard. |

An SBB driving trailer leading a push-pull train. |

The IC2000 double decker now in operation. |

A pre-production ICNeitech EMU under testing. |

In 2001 the Swiss Federal Railways will take delivery of 24 seven-car ICN tilting trains. |
|
| Baku-Tbilisi-Kars Line | ||
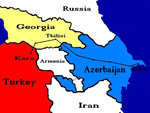
The Baku-Tbilisi-Kars (BTK) railway line is a regional railway link that will directly connect Baku in Turkey, Tbilisi in Georgia and Kars in Azerbaijan. |

Tbilisi is one of the cities served by the BTK railway. |

At Akhalkalaki station, a special area would be constructed for trains to convert from one gauge to another (1,520mm to 1,435mm). |
| Betuweroute Double-Track Freight Line | ||

Intensive passenger services on east-west sections like Eindhoven-Breda (pictured) have constrained freight operations. |

Seen at Dordrecht, east-west container traffic from Rotterdam and Kijfhoek yard should be re-routed along the Betuweroute. |

Special equipment has been installed on the Betuweroute to deal with incidents involving potentially hazardous cargoes. |

Strukton Railinfra played a major role in creating the Betuweroute and has now won the maintenance contract. |

Betuweroute commercial services were launched by Rail4Chem locomotives – this 'Class 66' carries I love Betuweroute flashes. |

Upon opening in June 2007, the line was not energised and junctions like this one at Geldermalsen were not in use. |

The Betuweroute's potential will be realised when multi-system locomotives like this Siemens ES64F4 are throughout on long workings. |

Planned extra line capacity east of the Betuweroute on the DB system is not yet available. |
|
| Brussels RER | ||

To the south-west of Brussels, Halle station was rebuilt for a role as a terminus for the forthcoming RER scheme. |

The modern development of Brussels has made it subject to high levels of commuter traffic from most directions. |

The North-South Junction line is the focal point of local, international and local passenger rail traffic in the Brussels area. |

The reworking of the Leuven line included increased capacity for RER traffic and segregation from through services. |

RER planning has taken into account the need for a high level of interchanges with other modes. |

The order for RER stock will mean the withdrawal of several old classes of electric multiple unit stock. |

At the heart of the 'European Quarter', Schuman station will be re-built and have extra access via the new tunnel towards Brussels Airport. |

Artist's impression of forthcoming Siemens Desiro ML stock; the first tranche will go to the Brussels RER. |
|
| Budapest Border Railway | ||

More than 15,000m² of noise protection walls have already been installed on this network. |

New electrical equipment replacing outdated systems. |

The old safety system equipment at Tata. |

The first electronic traffic control room in Hungary. |

'Fly eye' high luminosity red optics are now standard new safety features in use. |

The reconstructed station building at Tata. |
| Channel Tunnel Rail Link (CTRL) | ||

Eurostar at London Waterloo. The entire route of the rail link from London Waterloo to the mouth of the Channel Tunnel near Folkestone is 69 miles (108km) long. |

How the St Pancras International station entrance will look in 2007. |

An artist's impression of the entrance to the new Stratford station, where it will cross the London Underground's extended Jubilee Line. |

The roof of the new St Pancras station is under construction. |

New parallel lines for high-speed trains will soon change the appearance of many parts of east Kent forever. |

A Class 373 Eurostar passes Sandling on the ‘classic’ main line through Kent. |

The new Medway bridge under construction. |

The main earthworks of section 1. |

Construction on the Channel Tunnel rail link underway at Chilworth. |

Contractors working on the Channel Tunnel rail link section between the Medway bridge and the North Downs tunnel. |
||
| Crossrail, London | ||

Ongoing construction work for the Crossrail project at Moor House. |
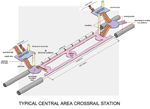
The layout of a typical Crossrail station in Central London. |

The remodelled exterior of Abbey Wood station. |

Crossrail can reuse the abandoned North London Line alignment (seen right) at Custom House, offering interchange with the Docklands Light Railway. |

The future equivalent of this Shenfield-bound train will be part of a Crossrail service using a tunnel beneath central London. |

Freight interests have expressed concern that Crossrail services will restrict freight services at busy locations such as Stratford on the Great Eastern main line. |

With new electrification east from Maidenhead, Thames Valley stopping services would be transformed as part of the Crossrail operation. |

The go-ahead for Crossrail was given in October 2007. |

In east London, Crossrail branches to the Great Eastern line (foreground) and Canary Wharf (left, background). |

Crossrail's south-eastern arm will add rail capacity at Canary Wharf to that of the Jubilee Line and Docklands Light Railway. |
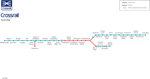
The modified Crossrail route. |

The western portals of the main tunnels beneath central London will be at Royal Oak near Paddington. |
| DART Underground/Interconnector Tunnel, Dublin | ||
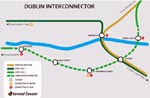
Proposed Interconnector line and stations with rail interchanges. |

More electrification will see some current Commuter DMU (railcar)-served lines joining the DART system. |

Luas Green Line terminus, St Stephen's Green will become a key interchange with the forthcoming Metro North and DART Underground. |

The northern Interconnector tunnel entrance will be in this area adjoining the Docklands development. |

The Interconnector tunnel will pass beneath the Liffey around a point as marked by the yellow line. |

Luas Red Line should operate past the development (right) from 2009, creating an interchange at Docklands/Spencer Dock DART Underground by 2015. |

Only DART services will use the Interconnector, as currently on the short section between Howth Junction and Howth. |

Joining the main line west of the terminus with extra tracks, the Interconnector will create a DART service west from Heuston to Hazelhatch. |

With electrification to Maynooth, the DART system will take over most services between there and Bray. |

DART trains from beyond Howth Junction (pictured) will use the Interconnector to reach Heuston and suburban stations on the Kildare line. |
||
| Dedicated Freight Corridor Project | ||
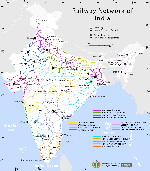
The dedicated freight corridor project will become part of India's already extensive railway service. |

The first two corridors, measuring 2,800km, will be finished by 2017. |
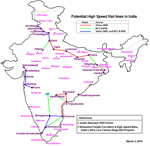
India is also planning a high-speed rail link. |
| Dublin-Navan Railway Line | ||

The Dublin-Navan railway line is expected to address the growing traffic problems in the region. |

The project is expected to be completed by 2015. |

Construction work being carried out on the Hansfield station. |
| East-West Rail Scheme | ||

Upgrading east of Oxford and a new connection beyond Bicester Town (pictured) is the core of the proposal to create a second Oxford-London route. |

Chiltern's Oxford services would enter London from the north-west serving High Wycombe and areas like Wembley and Harrow. |

Trains from Oxford would proceed from Bletchley (pictured) north to Milton Keynes or on the existing line to Bedford. |

The survival of Bletchley flyover (foreground) means that expense and conflict with West Coast Main Line traffic will be avoided. |

Chiltern's Marylebone route from Oxford would compete with high frequency bus services and First Great Western trains via Didcot (pictured) to London. |

Original Oxford-Cambridge infrastructure east of Bedford is unlikely to be restored - the former trackbed at Sandy on the East Coast Main Line. |
| Fegua Rail Network | ||
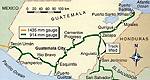
A new concession, awarded for 50 years, to reopen, restore and operate the entire 914 km rail network in the central American state of Guatemala, has been awarded to the Compania Desarrolladora Ferroviaria SA consortium, an affiliate of the Railroad Development Corporation (RDC) of Pittsburgh, USA. |

One of the Fegua-built diesels, dating from 1982, which is now in the hands of the Railroad Development Corporation. |

Guatemala is unusual in keeping steam power in reserve. |

The poor state of bridge structures is a major worry. |

The only traffic on Guatemala's railways during their closure has been the occasional handcart, run by enterprising private operators. |

One of the four operational General Electric diesel locomotives which it is hoped will be returned to traffic. |

This damaged bridge, at Villa Canales, gives some idea of the scale of the task facing the Railroad Development Corporation in reviving railways in Guatemala. |

At its height, FEGUA enjoyed a status as the most important rail network in central America. |

FEGUA provided links between the country's interior and the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. |
| Fehmarnbelt Link | ||

The Fehmarnbelt section of the Copenhagen-Hamburg rail service is currently provided by Scandlines train ferries. |
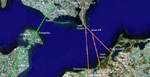
The Fehmarnbelt fixed link (in green) has won official support rather than the competing easterly Rostock-Gedser schemes. |

Made possible by the Great Belt crossing, the present Germany-Denmark continuous rail connection is via the Jutland peninsular (Rendsburg). |

Requiring diesel power, the service between Copenhagen-Hamburg (pictured) was for many years been provided solely by Danish IC3 units. |

With Hamburg-Lübeck (pictured) electrified, it leaves the section northwards to Puttgarden to be upgraded for the Fehmarnbelt project. |

Indicative of that project's success, more Bombardier dual system Contessa units were ordered for the Øresund fixed link in 2008 (Copenhagen). |

The Fehmarnbelt fixed link seems likely to become the main rail freight route between Scandinavia and the rest of Europe. |

A cable-stayed bridge is the favoured but not yet certain means of crossing the Fehmarnbelt. |
|
| Ferronorte | ||

Views of the spectacular new Parana River bridge. |

The line is designed with gentle curves and gradients. |

The dramatic expanse of the Parana River bridge. |

Ferronorte began the operation using second-hand locomotives from another Brazilian operator. |

Another second-hand locomotive used initially by Ferronorte. |

Brazilian manufacturer Maxion built a new fleet of aluminium-bodied wagons for Ferronorte, to transport soya beans. |
| Gatwick Express | ||

The new Class 460 driving cars boast a distinctive, aerodynamic front end. |

Gatwick Express trains run on existing track between London and the airport. |

The interior of the standard class area. |

There is an extensive luggage area for Gatwick Airport users. |

There is added luxury for first class passengers. |
|
| Gotthard Base Tunnel | ||

By avoiding the curves and spirals of the classic route, the Gotthard Base Tunnel will shorten journeys by 40km (South Ramp, Ticino). |

A mixed railway, capacity limits on the present Gotthard route mean that freight trains await paths at several points. |

Opened in 1882, the current 15km Gotthard tunnel will be retained as part of the Swiss network. |
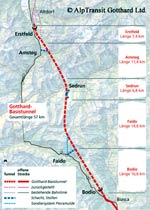
Old and new Gotthard rail routes. |

The twin south portal at Bodio close to where the old and new routes will join. |

Of the three projects on the Zurich-Milan axis, the Zimmerberg base tunnel has been postponed indefinitely. |

Access points to increase tunnelling progress and for emergency access was created at Sedrun. The projected Porta Alpina station has been shelved. |

Breakthrough by a tunnel boring machine of the Gotthard Base Tunnel. |
|
| Great Belt Fixed Link | ||

Great Belt location map. |

The new Oresund trains. |

The rail and road routes over the Great Belt. |

A works train traverses the DSB line between Funen and Zealand towards the East Tunnel's southern entrance. |

Each train has a unique 'Flex Front' system, which, along with the auto-coupling facility, allows up to five units to be quickly coupled. |

2nd class accomodation. |

The 8km East Tunnel comprises two parallel bores, lined with 62,000 concrete segments. |

The new railway station at Korsor. |

The final spans of the Øresund fixed link were in position in December of 1998. |

The spinning of the main cables for the East Bridge. |
||
| Hairatan-Uzbekistan Rail Project | ||

Construction work being carried out on the Hairatan-Uzbekistan rail project. |

A single, non electrified 75km rail track, where construction is in progress. |

A freight train from Uzbekistan stopping at Hairatan for offloading. |
| Hamersley Freight Line | ||
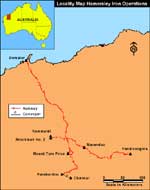
Hamersley Iron operations map. |

A BHP Dash 7 on a train for Finucane Island. |

A Hamersley Iron 70 Class (GE Dash 9) in action. |

A typical HI 105t capacity wagon. |

A trio of GM Dash 9 diesels haul one of the 23,500ton iron ore trains on the Hamersley Iron system under Pilbara Rail. |

Large stockpiles of raw iron ore are built up at key loading points for onward movement by rail. |
| Hanzelijn, Lelystad-Zwolle | ||

The Hanzelijn will run between Lelystad and Zwolle in the Netherlands. |
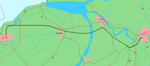
Passenger services on the Hanzelijn are expected to begin by the end of 2012, with rolling stock capable of travelling at speeds up to 200km/hr. |

The €10bn Zuiderzee Line between Amsterdam and Groningen plan has been cancelled, which means more passengers will depend on the Hanzelijn. |
| Heathrow Express | ||
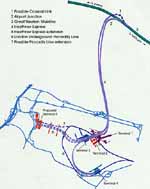
Heathrow Express route. |

Construction work on the 5-mile tunnel section of the line under the airport. |

A completed section of the 5-mile tunnel. |

Heathrow Express trains run for much of their journey along the Great Western main line. |

The trains' sliding doors, through which access onto and off of platforms is almost level. |

The Heathrow Express. |

Heathrow Express passenger coach interior. |

Heathrow Connect serves intermediate stations as well as the Heathrow Express terminals. |

Heathrow trains are maintained under contract by Siemens at their Old Oak Common depot. |
| Hong Kong East Rail | ||

Containerised freight is a major area of growth on the East Rail system. |

The new Automatic Train Protection system demands constant monitoring by highly-trained control room staff. |

Improved maintenance and refurbishment help ensure KCRC's rolling stock meets the growing demands on it. |
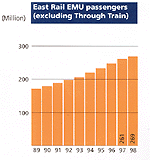
The continued year-on-year growth in East Rail's passenger numbers during the 1990s. |

The new KTT cross-border trains have brought substantial increases in traffic to the East Rail network. |

State-of-the-art facilities at the thoroughly refurbished Hung Hom station. |
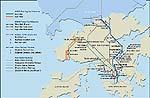
A map of KCRC's future and present rail networks. |
||
| Hong Kong West Rail | ||
The West Rail route. |

Station concourses incorporate automated ticketing systems. |

Sufficient lifts and escalators allow for ease of passenger handling. |

Platforms have straight boarding areas with minimum platform gap as well as platform screen doors. |

Cross section configuration of a typical West Rail station. |

West Rail will be one of the quietest railways in the world. |

The interior of the trains are spacious and able to carry 335 passengers. |

The trains will be formed of 7 cars, due for delivery during 2001. |

11.5km of the new line will be in tunnel. |

The first new train is delivered to the Hong Kong West Rail project. |
||
| Hudson Rail Tunnels – New Jersey/New York | ||

The new Hudson River rail tunnel will be used by both NJ Transit commuter trains and Amtrak services off the Northeast Corridor. |

A mixture of diesel and electric powered services are currently in service. New dual-power trains are expected to enter service when the new tunnel opens in 2018. |

New York Penn Station has reached capacity. As part of the project a new station will be built next to it at 34th Street in Manhattan. |

Commuters form the bulk of the passengers using NJ Transit services to cross the Hudson River to reach their place of work. The new tunnel will shorten their journeys and reduce overcrowding. |

Artist's impression of the new Bombardier diesel-electric hybrid loco as ordered by NJ Transit in August 2008. |
|
| Hunter Valley Rail Freight Corridor | ||

Expansion of the Hunter Valley rail freight network will increase coal delivery capacity from Hunter Valley coal mines to the Port of Newcastle in New South Wales, Australia. |

ARTC has formed the Hunter 8 Alliance with John Holland Pty Ltd and GHD Pty Ltd, to design and construct the Maitland to Whittingham third track. |

The Hunter Valley rail network upgrade is a part of the Australian Government's Nation Building Economic Stimulus Plan. |
| Indonesia Private Railway Freight Corridor | ||
Map of Indonesia. |
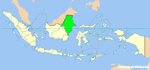
The 130km freight corridor will be located in the East Kalimantan province in Indonesia. |
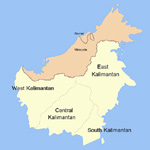
The East Kalimantan province is rich in mineral resources. |

The new railway line will transport coal from Muara Wahau mine in East Kutai region to a port terminal at Bengalon. |
||
| Ipoh-Padang Besar Electrified Railway Project | ||

The construction of the tunnel at Bukit Berapit. |

The construction of a marine viaduct at Bukit Merah. |

Construction of one of the double track bridges. |
| Karachi Circular Railway Revival | ||

A model of the train to be used for the KCR. |

The old KCR operated until the late 1990s. |
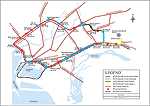
The route map of the KCR. |

A proposed station at Shaheed-e-Millat. |

All the proposed stations of the KCR will have a design similar to the Shaheed-e-Millat station, with modifications depending on the elevation of the station. |
|
| Kashmir Railway | ||

The Kashmir Railway is being built through the inhospitable terrain of the Himalayan foothills. It will also cross the Chenab River on the world's highest railway bridge. |

Indian Railway's network is always busy, as rail is a convenient way to travel compared to road. The Kashmir Railway will provide a reliable connection to the isolated area. |

A total of 30 stations are being built along the line to serve the communities that line the route. |

Trackwork is a major task on the Kashmir Railway, partly due to the harsh weather and terrain. Completion of the full 290km line is planned for 2016. |
||
| Kowloon-Canton Railway | ||
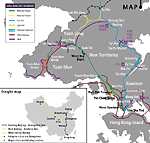
This intense traffic on the Kowloon-Canton heavy rail system has driven a scheme to build two new branch lines, between Ma On Shan and Tai Wai, and an extension from Hung Hom to Tsim Sha Tsui. |

A through train from the Chinese mainland near the Kowloon-Canton University station. |

The AEG/Adtranz locomotive design, based on the Swiss Lok 2000, is being ordered for Kowloon-Canton services. |

Each rake of coaches comprises five standard class coaches and one first class vehicle, and is powered by a locomotive type derived from the Lok 2000 design. |

KCR Freight has been mounting a concerted effort to attract more traffic, with new one-price tariffs. |

Five Siemens Series 8000 Eurorunner diesel locomotives are now in service with the Kowloon-Canton Railway on freight services. |

Kinki Sharyo SP150 stock for the Ma On Shan line. |

Interior of Kinki Sharyo EMU for KCR West Rail. |

East Rail refurbished GEC-Alsthom stock at Kowloon Tong. |
| Lantau Line and Airport Railway, Hong Kong | ||
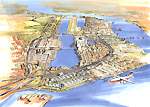
Artist's impression showing the dramatic impact of the Airport Express and Lantau Line on the landscape. |

Translucent noise barriers have been installed in sensitive areas. |

The spectacular Tsing Ma suspension bridge was an Anglo-Japanese construction project. |
| Lanzhou-Chongqing Rail Project | ||

The Lanzhou-Chongging is a 832km long rail development project. |

The Lanzhou-Chongging line will have 285 bridges. |

The line will also include 12 super long tunnels of more than 10km. |
| Leipzig City Tunnel | ||

One of Europe's largest stations, Leipzig's terminus layout has limited its potential in terms of urban and local services. |

The twin bores of city tunnel were driven from the southern end by the same TBM. |

A large area around the Hbf at the city's northern edge has undergone reconstruction to accommodate the new sub-surface station. |

By 2011 Leipzig should gain an intensive heavy rail service through the centre as per Stuttgart, Frankfurt Main and München (pictured). |
||
| London Overground Suburban Network | ||

National Rail signage across 20 London boroughs will give way to TfL Overground branding. |

Long-serving Class 313 units were taken over for London Overground operations in November 2007, pending replacement by 2009. |

TfL closes Whitechapel-New Cross/New Cross Gate in December 2007. Upgraded and extended as an Overground route, it will reopen in 2010. |

Single and dual system Bombardier's Class 378 trains (similar to this Class 376 seen at New Cross) will be the main Overground rolling stock by 2010. |

Class 378s are likely to feature longitudinal seats and high-density interiors, although some may have a layout similar to this Class 376. |

First-generation Sprinter Class 150, as seen at Barking, should be replaced on ‘Goblin’ services by new Class 172 from 2009. |

The former Silverlink service between Willesden Junction and Clapham Junction (pictured) is now part of TfL Overground. |

Like all stations acquired by TfL Overground, Gospel Oak will be deep-cleaned and re-branded. |
|
| Lötschberg Base Tunnel | ||

Long-distance freight on the Basel-Milan axis was the prime rationale for the Lötschberg Base Tunnel project (Muttenz marshalling yard, Basel). |

Safe transport and disposal of spoil was a major issue for the developers. |

Tracks rise on parallel viaducts to the twin tunnels at Raron from the SBB Rhone Valley line west of Visp. |

Domestic express services over the new line are by federal operator SBB. |

Obviating trackside signalling and requiring suitably fitted stock, ETCS Level 2 was built into the new Lötschberg tunnel. |

A large area at Frutigen was redeveloped for the junction of the new and original lines just beyond the north portal. |

Including intermodal and RoLa trains on Lötschberg lines, Swiss-based HUPAC is the main body for freight handling across the Alps. |

BLS stopping services over the old line are re-equipping with new panoramic multiple unit stock from late 2008. |
|
| Madrid Barajas Airport Rail Link | ||

Airport rail links are becoming increasingly popular. Madrid Barajas Airport will have its own from 2010. |

Airport links generally have dedicated train fleets. |

Specially-designed luggage racks help passengers store bulky cases on the journey. |

The Barajas Airport Rail Link will use both new alignments and existing infrastructure, as the Gatwick Express does in the UK. |

Barajas Airport has expanded greatly to become Europe’s fifth busiest. |
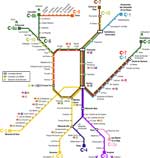
System map. |

The airport link will join RENFE’s Cercanias network for Madrid. |
||
| Matara-Kataragama Railway Line | ||

Civil works being carried out for the sub-station at Weharahena. |

Path being cleared for laying the tracks for Stage I. |

Alternative land arranged for the people at Palliyaguruwattha. |

Alternative land arranged for the people at Palliyaguruwattha. |

Construction of Niwala Bridge. |
|
| Mpumalanga to Richards Bay Freight Coal Line | ||

Richards Bay is a significant port that requires excellent transport connections. |

Coal is a vital export commodity in South Africa, so suitable freight transport is essential. |
Mpumalanga has 44 coal-rich mines that require excellent freight transportation in the form of a rail line. |
Transnet maintains an extensive rail network across South Africa, connecting it to other areas in the sub-Saharan region. |
||
| Netherlands | ||

Netherlands railways has started commissioning trials for its four multi-system ICE three trainsets. |

The Rotterdam electronic interlocking. |

IRM-double deck EMU running on the Netherlands Network. |

The Netherlands infrastructure includes many bridges due to the high water to land ratio. |

Standard Modern Intercity 'IC3 unit' with raised cabs and through gangways. |

A Netherlands Railways 'Koploper' train at speed. |

French influence abounds in the Netherlands - this locomotive is one of 58 electric locomotives built by ALSTOM between 1981-83. |

Modern passenger stock in Amsterdam Centraal station - a push/pull trailer stands alongside a locomotive-hauled train. |

A DM 90 diesel-hydraulic multiple-unit train set for Netherlands railways. |
| Network Rail | ||

Trent Valley and Stafford remodelling will segregate high speed services from freight and local passenger paths. |

Commercial development above NR managed London Canon Street, with EWS-hauled test train. |

NR-managed Edinburgh Waverley, subject to a major track remodelling project. |

First GBRf manages NR Whitemoor Yard at March, Cambridgeshire. |

Electrification gaps cause lengthy diesel haulage under wires: Biggleswade, Bedfordshire. |

Improved station access: Class 158 between newly installed ramps at Barnetby, Lincolnshire. |

Bringing more work 'in-house', NR has scaled back on its use of contractors. |

One of NR's own vehicles at work on their largest project, the West Coast Main Line. |

NR has a portfolio of structures like Bristol Temple Meads that are part of the nation's architectural treasures. |

Leeds station, managed by NR, is a completed major project where rebuilding also included track and signalling. |
||
| North Bengal-Sikkim Railway Link | ||

The rail link will cut through mountains and valleys to connect Sikkim to the main Indian rail network for the first time. |

There will be four manned level-crossings along the 57.2km route. |

Tunnels are a big feature of the planned route – 70% of the line will be underground. |
| North Korea-South Korea Railway | ||

South Korea has a mainly modern system, including multiple units. |

North Korean rolling stock and locomotives were mainly provided by Russia. |

Smaller locomotives and shunters in the north are also from Russia. |

Map of North and South Korea and the Soeul-Pyongyang railway. |
||
| North-South Railway Line | ||
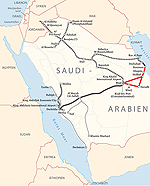
Current rail links in Saudi Arabia, showing how the North-South Railway will link Riyadh with Al-Haditha. |

4300HP diesel locomotives, similar to this BNSF train, will operate on the North-South Railway. |

The North-South Railway will provide crossing through the Al-Nafude desert, pictured, from Riyadh to Al-Haditha. |
| North-South Transnational Corridor, | ||
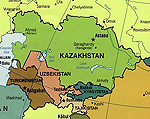
The North-South Transnational Railway line will connect two central Asian countries-Kazakstan and Turkmenistan to Iran. |

The North-South Transnational Corridor will be 677km long. |

Road transport in Turkmenistan is inadequate and unsafe. |
| Northern Ireland Railways Revitalisation | ||

Opened in 1994, Belfast's Dargan Bridge improved rail links to the north and indicated some faith in the future of Northern Ireland's railway system. |

There are hopes that increased frequency on the Belfast-Dublin 'Enterprise' route may help rebuild passenger levels. |

The small locomotive fleet includes two Class 201s for Enterprise workings. NIR's 209 seen at Dublin Heuston rather than the usual Connolly terminus. |

Somewhat distant from the centre in spite of the name, Belfast Central connects most NIR services. |

The Great Victoria Street terminus is sited in Belfast city centre. |

After years of under-funding, most NIR routes have had some track, station and signalling upgrades. |

The Metro brand is used by NIR's sister organisation operating Belfast's main bus service. |

With a twice-hourly Belfast service after line upgrading, the well-tended Carrickfergus station has improved passenger access and information displays. |

The 23-strong CAF 'C3K' fleet has greatly improved standards for passengers. |

Doubling jointly operated cross-border frequencies may be achieved by using modern DMU stock like NIR's C3K or Irish Rail's Class 22000. |
||
| Norway | ||

The new face of high-speed travel in Norway, the Class 73 electric multiple unit. |

Sweden's X2000 tilting train is the forerunner of neighbouring Norway's own new trains. |

A diagram of the tilting technology employed on Norway's Class 73 electric trains. |
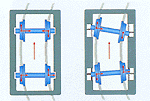
A demonstration of the benefits of the trains' self-steering wheel axles. |

A focal point for local, regional and long-distance trains, Oslo Sentralstasjon (Oslo S) is by far Norway's largest station. |

The 36 Ansaldobreda BM72 EMU sets were a marked styling change over NSB's previous commuter trains. |

Earlier generations of commuter stock have been refurbished to extend their working lives. |

Part of the Talbot-developed 'Talent' family, like this DB Class 643, the NSB BM93 is a tilt-equipped, low-density two-car variant for mid-range routes. |

Non-tilt BM71 sets that work a 19min service between Oslo and Gardermoen airport are due to be extended to four coaches. |

After initial serious faults were resolved, two versions of the tilt-equipped BM73 have become the mainstay of regional and long distance services. |
||
| Obskaya–Bovanenkovo Railroad, | ||

The Obskaya–Bovanenkovo railroad is being build to improve transport facilities to the Yamal Peninsulas. |

The railroad in Russia is being constructed by Gazprom. |

The railroad will help to deliver materials and equipment for Gazprom's Bovanenkovo field development. |

Construction of the bridge crossing over the Yuribei River was undertaken in harsh climatic conditions. |

Lokomotiv-Leasing will supply 20 TE33A diesel locomotives to run on the railroad. |
|
| Parramatta-Chatswood Rail Link | ||

The Parramatta rail link's major benefits are seen as the opening up of business and employment opportunities in North Ryde and the lower North Shore for residents of western Sydney and the Central Coast. |

Trains on the new route will be integrated with existing commuter services, such as seen here at Granville level crossing. |

Rydalmere station is one of those expected to be upgraded as part of the infrastructure works. |

An artist's impression of the Parramatta line's main new crossing, of the Lane Cove River. |

Sketch of one of the main rail-bus interchanges, with the Liverpool-Parramatta rapid bus transitway. |

The modern and sophisticated Millenium Trains for Sydney’s CityRail services. |

The Millenium Trains entered service in 2002, but were withdrawn for a year for modifications. |

Millenium Train in service: two new double-deck Downer EDI built units pass on the CityRail system. |
|
| Qinghai-Tibet Heavy Rail Line | ||

Golmud Station; from here the line stretches 1,142km to Lhasa. |

Xinhua bridge; one of the main viaducts on the Qinghai-Tibet railway. |

Inside one of the Chinese-made 25T carriages. |

Tanggula Station, at 5,068m above sea level, is the world's highest railway station. |

The diesel locomotives in use on the Golmud to Lhasa line were made by GE in Pennsylvania. |

Liuwu; the last tunnel before arriving at Lhasa station. |

Lhasa Station, Tibet – a rail journey of 1,956km from Xining, capital of China's Qinghai province. |

The Lhasa Valley in Tibet, with Sera Monastery in the foreground. |
|
| Quebec-Windsor Corridor | ||
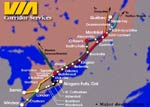
Map of the Quebec-Windsor corridor. |

The rugged landscape of more remote parts of the Quebec-Windsor corridor, as seen here, illustrates why line upgrading is proving such a difficult project. |

The contrast between older generation locomotives and newer rolling stock used on the Quebec-Windsor corridor services is obvious. |

The Metropolis Trainset. |

The trains present an unusual sight against the modern Toronto skyline. |

The Ocean Trainset. |

A Viarail train enters the outskirts of Montreal. |

Decades-old signalling still controls much of this part of the network, but service reductions over many years mean it is sufficient to cope with present-day demands. |

Some services still use observation cars, to allow passengers good views of the dramatic scenery. |
| Rijn Gouwelijn | ||

Eastern terminus of the future Rijn Gouwelijn and the trial operation, Gouda is on the NS Utrecht-Den Haag route. |

At intermediate station Waddinxveen, separate low-level platforms were added for the tram vehicle service. |

Western tram service terminus is Alphen aan den Rijn, with heavy rail connections to Leiden and Utrecht. |

The A32 unit interior contrasts markedly with the NS heavy rail stock it replaced between Gouda and Alphen aan den Rijn. |

Leiden citizens registered their opposition to the Province's original routing of light rails through the city's streets. |

Rijn Gouwelijn's busiest stop is likely to be at Leiden Centraal station on the Amsterdam-Den Haag-Rotterdam main line. |

Famed for academic institutions, Leiden's entirely new light rail line will serve this area by Centraal station. |

Promoters refer to the nearby RandstadRail's tram-trains to indicate the nature of vehicles to be deployed on Rijn Gouwelijn. |
|
| Scottish Borders Railway Waverley Project | ||
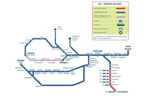
Transport Scotland is constructing a 49km railway line from Edinburgh Waverley to Tweedbank in the Scottish Borders. |

The Edinburgh Waverley railway station. |
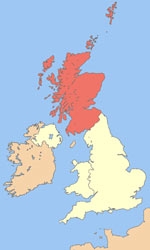
The project will bring environmental benefits to Scotland by reducing car journeys by more than 700,000 a year. |
| Shah-Habshan-Ruwais Railway, | ||
The Shah-Habshan-Ruwais project is the first phase of the UAE national rail network. |

The Shah-Habshan-Ruwais is a 264km long rail route. |

The project will have 250 covered hopper wagons. |
| Tbilisi Railway Bypass Project | ||
Tbilisi is the capital of the Republic of Georgia. |

Tbilisi Railway Bypass is a 10km long restructure project. |

The east-west oil corridor transported 10m tons of crude oil in 2008. |
| Thameslink 2000 | ||

Map of the Thameslink 2000 rail network. |

In the early days of the service, trains ran into St Pancras main line terminus. From 2006, they will use a new station, under this site. |

One of the most spectacular features of the modernised route through London is this new bridge across Borough High Street. |

Blackfriars station, where two new through lines will be created and the canopy extended over the River Thames. |

Borough Viaduct - the green line shows the new alignment of Thameslink 2000. |

Farringdon: Proposed view of the new frontage along Cowcross Street. |

An artist's impression of the new concourse at London Bridge station. |
||
| Vallarpadam Railway Link | ||

The Vallarpadam railway link is the longest rail bridge in India built in Kochi, Kerala state. |

The Vallarpadam railway link will be exclusively used for goods container traffic to and from ICTT. |

Work on the bridge started in October 2007 and was completed in March 2010. |

About 80% of the Vallarpadam bridge is constructed over the backwaters of Vembanad lake. |

The latest construction technology such as launching girders machines and concrete pumping were used during bridge construction. |
|
| Welsh Highland Railway Project | ||

NG / G16 Beyer-Garratt No.143 as it enters the Aberglaslyn Pass with a train to Hafod y Llyn. |

Aberglaslyn Pass and Beddgelert seen from the top of Bryn Du, as NG / G16 Beyer-Garratt No. 143 heads south with a train to Hafod y Llyn. |

NG / G16 Beyer-Garratt No. 143 steams through the tunnels in the Aberglaslyn Pass. |

The interior of a standard Welsh Highland Railway carriage. |
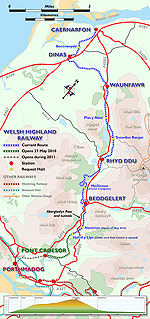
Detailed Welsh Highland Railway map 2010. |
|
| Western Railway Corridor Project, Ireland | ||

Staff pulling the long-welded rails onto the concrete sleepers between Athenry and Craughwell. |

The N18's automatic barrier level crossing and rebuilt overbridge. |

The newly built Ardrahan station. |

Inaugural train services from Gort station. |

Inaugural train leaving Gort station. |
|
| Zurich Rail Capacity Increase | ||

Zurich HB is at the heart of the Durchmesserlinie project that will have effects on regional and national services. |

Apart from the 1991 S-Bahn platforms, all traffic must enter and leave HB from the western end. |

The Re 450/DPZ formations were an early response to growing rail demand around Zurich city and canton. |

A tunnel opened in 1991 gave the initial low-level Zurich HB S-Bahn platforms greater capacity and operating flexibility. |

Zurich HB's destination board illustrates the intensity of S-Bahn services over a short period. |

Zurich HB 'Sihlpost' platforms 51–55 are a temporary measure to add extra capacity pending completion of the Durchmesserlinie project. |

Entering service from 2006, the Siemens RABe 514 is the second generation of high capacity Zurich S-Bahn stock. |
||


