Hyderabad Metro, India
|
The Hyderabad Metro is a proposed rapid transit system for the city of Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India. The project, owned by Hyderabad Metro Rail, was proposed in 2008 to meet the growing transport needs of the city's growing population, which is expected to increase to 13.64 million by 2021. The contract to build and operate the metro system was awarded to Larsen and Toubro (L&T) in July 2010. The city covers the municipal corporation and metropolitan areas of the region. The municipal corporation area is about 625km² while the metropolitan area covers 6,852km². Buses are the major public transportation system in Hyderabad, and are operated by the Andhra Pradesh Road Transport Corporation, which runs a fleet of more than 19,000. Hyderabad also has a light rail transportation service, the Multi-Modal Transport System. Journeys by public transport are estimated to be 42% of all motorised trips made per day. However, with growing population and vehicles on the road, the city's transportation system has come under immense pressure to develop metro rail project. The new metro rail will shorten journey time by 50-70% and is expected to reduce carbon emissions by up to 3,100t a year. "The estimated cost of the Hyderabad Metro project is $2.62bn."
Finance The estimated cost of the Hyderabad Metro project is $2.62bn. About 20% of this will be provided under the government’s viability gap funding scheme. The federal and state governments will provide financial support for 40% of the project cost. Project In April 2008, the Government of Andhra Pradesh (GoAP) approved phase I of the project based on traffic and transportation reports generated by the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC). The DMRC's reports were based on studies made of the geophysical features of the routes and on international best practices and economics. Phase I will include three lines along high-density traffic corridors, spanning 71.16km. In July 2008 the GoAP awarded a contract to executing the project under a design, build, finance, operate and transfer basis for 35 years to a consortium led by Maytas Metro. However, this contract was cancelled in July 2009. "Phase I will include three lines along high-density traffic corridors, spanning 71.16km."
The state government subsequently invited request for qualification bids; L&T emerged as the lowest bidder at INR1.46bn, and was awarded the contract under a design, build, finance, operate and transfer basis. The unsuccessful bidders were the Transstroy-OJSC Transstroy-CR18G-BEML consortium, with a bid of INR2.2bn, and the Reliance Infra-Reliance Infocomm consortium, with a bid of INR2.9bn. L&T will receive real estate construction rights over 18.5 million ft², in addition to ticket sales revenue. The project is expected to achieve financial closure in six months. Groundbreaking is scheduled for the end of 2010, and completion is slated for 2018. Line routes The Hyderabad Metro will have three lines. Corridor-1 will run from the south-east to the north-west of the city and will be 29.87km long, connecting 27 stations between Miyapur and LB Nagar. Corridor-2 will run from east to west and will be 14.78km long, connecting 16 stations from Secunderabad to Falaknuma. Corridor-3 will run from north to south and will be 26.51km long, connecting 23 stations from Nagole to Shilparamam. All three lines will interconnect at common stations; Ameerpet on lines one and three, the medical college on lines one two, and the parade grounds on lines two and three. All stations will be 1km apart on average. Infrastructure The Hyderabad Metro will be an elevated system with a 9m-wide bridge structure. The bridge will run from the central median of the road and will have two tracks. The tracks will be 1,435mm standard gauge. The system's electrical traction will be of DC 750V and power will be supplied through the third rail. Continuously welded rails will be laid to minimise the noise levels. "Continuously welded rails will be laid to minimise the noise levels."
Trains will be operating at a top speed of 80km/h.The locomotives will be air-conditioned and will include automatic doors and other safety features. The metro system will also have a feeder bus service. The buses will be air-conditioned and will connect nearby lanes, businesses and other popular destinations. Smart card-based automatic ticketing and gate systems are planned for the metro. Signalling and communications Trains will have automated systems such as automatic train control and automatic train protection. Automatic train operation will also be upgraded. As part of the concession agreement, automatic systems have to be constructed, operated, maintained and transferred at the end of the concession period. |
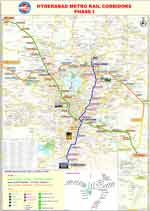  Expand Image Expand ImageThe rail corridors of the Hyderabad Metro. |
  Expand Image Expand ImageThe population of Hyderabad is expected to increase from 7.8 million to 13.64 million by 2021. | |
  Expand Image Expand ImageJourneys by public transport are estimated to be 42% of all motorised trips made per day. | |
  Expand Image Expand ImageThe Hyderabad Metro will be an elevated system with a 9m-wide bridge structure. |


